android视图组件之ListView
ListView是android系统中比较常用的视图组件,它的构建主要包含两方面信息:分别是UI组件的绘制和数据源的设置。UI组件和数据源之间通过适配器建立关联。这里的适配器充当媒人的角色,在为UI组件和数据源介绍亲事之前,媒人需要对双方有所了解,了解的内容包括:ListItem的布局信息和数据源的实体信息。
常用的适配器有两种,分别是ArrayAdapter和SimpleAdapter
ArrayAdapter的应用场景:
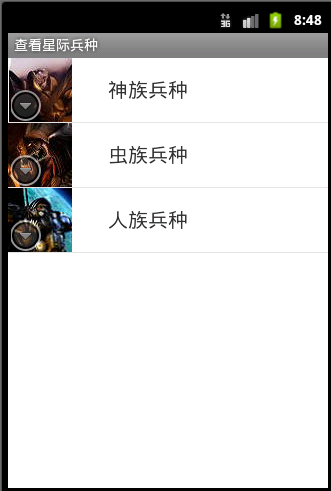
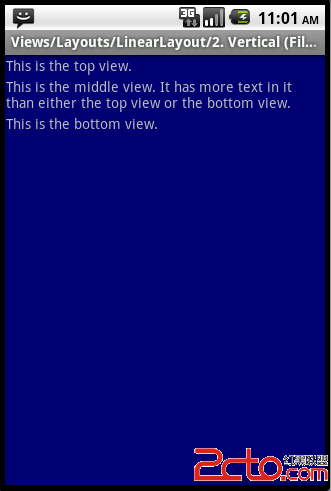
ListItem显示单一,只需显示一条文本信息即可
示例图:
针对这种显示方式,android系统为我们提供了默认的ListItem布局
res\layout\simple_list_item_1.xml
[html]
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@android:id/text1" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceListItemSmall"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:paddingLeft="?android:attr/listPreferredItemPaddingLeft"
android:paddingRight="?android:attr/listPreferredItemPaddingRight"
android:minHeight="?android:attr/listPreferredItemHeightSmall"/>
该布局定义了一个TextView用于显示ListItem的文本内容,构造ArrayAdapter之前,只需将该TextView的id和布局文件id作为参数传递至ArrayAdapter的构造参数中即可。
[java] view plaincopy
new ArrayAdapter<Word>(context,android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,android.R.id.text1,List<?> dataSource);
第四个参数表数据源信息,TextView要显示的文本内容即为List集合中实体元素的toString()值。
如果我们想自定义ListItem布局以便ListView的显示更加丰富,那么我们经常会用到另外一种适配器SimpieAdapter。
SimpieAdapter的数据源呈如下结构:List<Map<String,Object>>,List集合中不再是实体对象,而是一个Map,Map.Entry会和ListItem进行绑定,而Map的Value值会映射到ListItem的显示内容中去。
假设,我们构造了如下ListItem布局:
[html]
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/fileItem_image"
android:layout_width="32dp"
android:layout_height="32dp"
android:layout_margin="4dp"
android:contentDescription="@string/img_desc"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/fileItem_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/fileItem_path"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
又提供了如下数据源信息:
[java]
List<Map<String,Object>> fileList=new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>();
Map<String,Object> fileInfo=new HashMap<String,Object>();
fileInfo.put("img",R.drawable.img);
fileInfo.put("name","fileName");
fileInfo.put("path","filePath");
fileList.add(fileInfo);
便可通过如下构造器构建SimpleAdapter对象
[java]
new SimpleAdapter(context, fileList, R.layout.filelist_item, new String[]{"img", "name", "path"},
new int[]{R.id.fileItem_image, R.id.fileItem_name, R.id.fileItem_path});
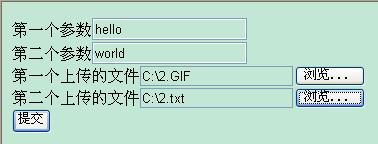
由构造器可以看出,img、name和path分别和fileItem_image、fileItem_name和fileItem_path三个组件形成映射,它们的value值将会显示到3个组件的文本内容中去。
显示效果: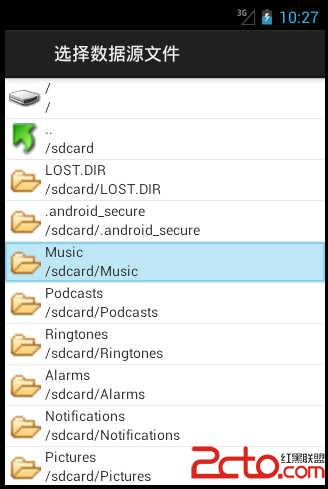
ListView组件可监听如下事件:
选择:setOnItemSelectedListener
单击:setOnItemClickListener
长点击事件:setOnItemLongClickListener
长点击显示contextMenu:setOnCreateContextMenuListener
补充:移动开发 , Android ,